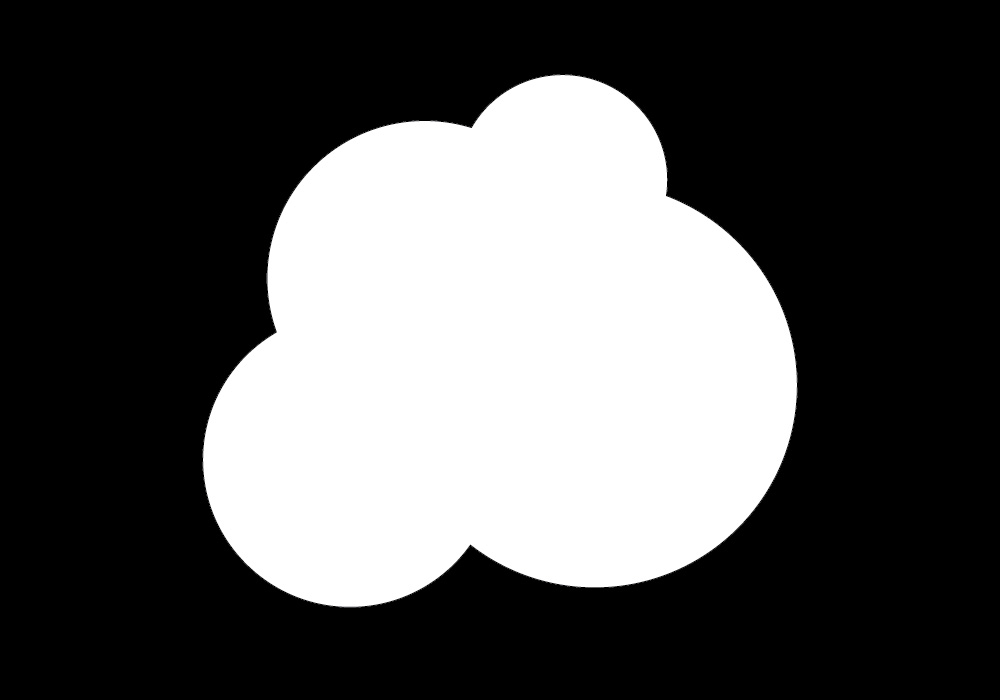

In the above examples we are using the pixel color of an image rather than the sketch boundaries as the limit for Brownian motion. We are testing the image for black pixels rather than the outer dimensions of the sketch to determine whether to reverse the direction of the next point position.
Here is the initial code to test for the sketch boundaries:
float ranx = random(-5,5);
float rany = random(-5,5);
if(p.x + ranx > width || p.x + ranx < 0){
ranx = -ranx; }
if(p.y+ rany > height || p.y + rany < 0){
rany = -rany;
}
The new code checks the color of the image pixel in the next position. If the brightness of the pixel is less than 100 then it is black and the next point position is reversed.
float ranx = random(-8,8);
float rany = random(-8,8);
color cx = image_holder.get(int(p.x + ranx), int(p.y));
color cy = image_holder.get(int(p.x), int(p.y+rany));
if(brightness(cx) < 100){
ranx = -ranx;
}
if(brightness(cy) < 100){
rany = -rany;
}
Here is the code for the sketches above:
ArrayList <Searcher> image_searchers = new ArrayList <Searcher>();
//declare PImage object
PImage img;
//declare PGraphics object to hold image
PGraphics image_holder;
void setup(){
size(1000, 700);
img = loadImage("boundary_1.jpg");
image_holder = createGraphics(1000, 700);
image_holder.beginDraw();
image_holder.image(img, 0, 0);
image_holder.endDraw();
}
void draw(){
background(0);
for(int i = 0; i < image_searchers.size(); i++){
Searcher is = image_searchers.get(i);
is.display();
is.update();
}
}
//function to allow for a searcher to be added on mouse click
void mouseClicked() {
color c = image_holder.get(mouseX, mouseY);
//check to see if the position of the mouse is in a white or black pixel
//only add if a white pixel is clicked on
if(brightness(c) > 100){
image_searchers.add(new Searcher(mouseX, mouseY));
}
}
class Searcher {
ArrayList <PVector> position = new ArrayList <PVector>();
ArrayList <PVector> collisions = new ArrayList <PVector>();
FloatList pscale = new FloatList();
Searcher (float x, float y) {
float xpos = x;
float ypos = y;
position.add(new PVector(xpos,ypos,0));
pscale.append(15);
}
void display() {
noStroke();
for(int i = 0; i < position.size()-1; i++){
PVector p = position.get(i);
PVector p2 = position.get(i+1);
stroke(0,255,255,100);
line(p.x,p.y,p2.x,p2.y);
float sc = pscale.get(i);
fill(255,100);
noStroke();
ellipse(p.x,p.y,sc,sc);
pscale.set(i,sc*0.99);
}
for(int i = 0; i < collisions.size(); i++){
PVector p = collisions.get(i);
fill(255,0,0);
noStroke();
ellipse(p.x,p.y,5,5);
}
}
void update() {
PVector p = position.get(position.size()-1);
float ranx = random(-8,8);
float rany = random(-8,8);
color cx = image_holder.get(int(p.x + ranx), int(p.y));
color cy = image_holder.get(int(p.x), int(p.y+rany));
float col = 0;
if(brightness(cx) < 100){
ranx = -ranx;
col = 1;
}
if(brightness(cy) < 100){
rany = -rany;
col = 1;
}
if(col == 1){
collisions.add(new PVector(p.x,p.y,0));
}
float newx = p.x + ranx;
float newy= p.y + rany;
position.add(new PVector(newx,newy,0));
pscale.append(15);
}
}