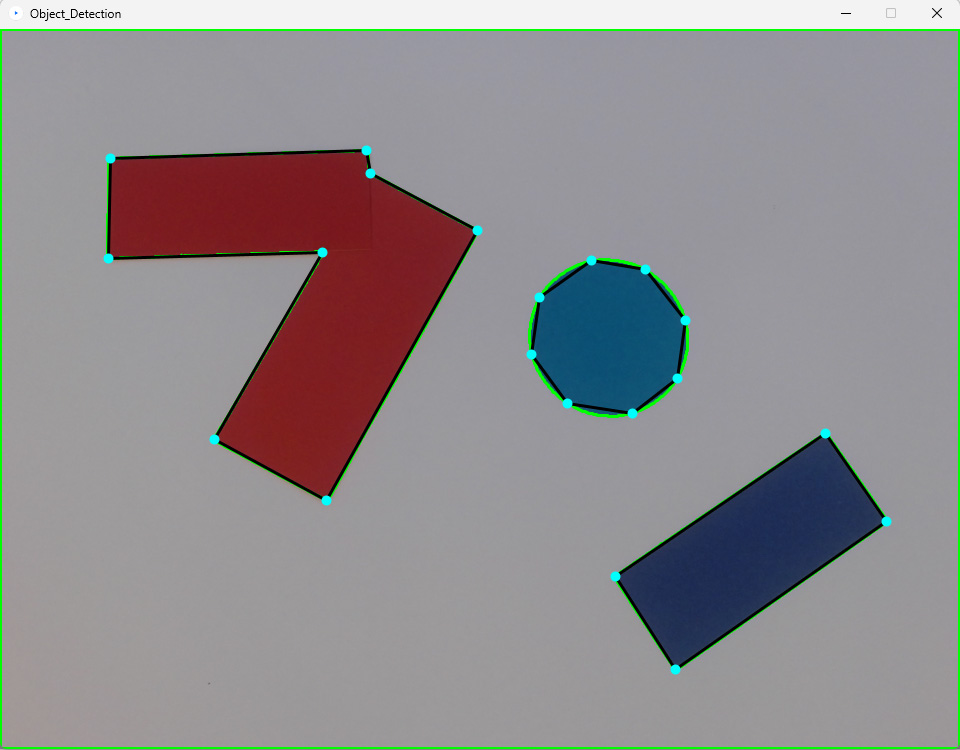
Using a camera and the OpenCV library you can get the contours or boundary of physical objects or shapes. The first thing you will need to do is install the library. The library has many tools to adjust and analyze images. We are going to be retrieving the contours of an image using the FindCountours command found in this OpenCV example.
There are a couple of things to keep n mind. We are using a video camera rather than a static image. OpenCv converts the image to black and white so you can detect shapes through the images luminosity, but not by individual color. You can use a threshold to convert the image to only pure white and pure black to contour the shapes.
Below is the code to load the library. and the variables we will need.
import processing.video.*; import gab.opencv.*; //list to store the contours for each object ArrayList contours; ///declare OpenCV object OpenCV opencv; //video capture opject Capture cam; PGraphics image_holder; PImage bwim,conim; int w = 960; int h = 720;
Once you have the libraries imported and the variables declared we need to initialize the camera in the setup.
void setup() {
size(960, 720);
String[] cameras = Capture.list();
// The camera can be initialized directly using an
// element from the array returned by list():
//you can also set a custom resolution
cam = new Capture(this, 960,720,cameras[0]);
cam.start();
image_holder = createGraphics(w, h);
}
Unlike the contour example we will be reinitializing the OpenCV object every frame in the run function because our image is changing every frame. The below code shows the various image adjustments we are doing with OpenCV before we retrieve the contours.
import processing.video.*;
import gab.opencv.*;
//list to store the contours for each object
ArrayList contours;
///declare OpenCV object
OpenCV opencv;
//video capture opject
Capture cam;
PGraphics image_holder;
PImage bwim,conim;
int w = 960;
int h = 720;
void setup() {
size(960, 720);
String[] cameras = Capture.list();
// The camera can be initialized directly using an
// element from the array returned by list():
//you can also set a custom resolution
cam = new Capture(this, 960,720,cameras[0]);
cam.start();
image_holder = createGraphics(w, h);
}
void draw() {
//check to see if the camera is available
//before you read an image ftom it
if (cam.available() == true) {
cam.read();
}
scale(0.5);
//load the image into the image holder
//this allows you to analyze the image even
//if you are not displaying it
image_holder.beginDraw();
image_holder.image(cam, 0, 0);
image_holder.endDraw();
//initialize the OpenCv object and use the capture
//object to retrive the image form the camera
opencv = new OpenCV(this, cam);
opencv.loadImage(cam);
opencv.gray();
bwim = opencv.getSnapshot();
opencv.threshold(90);
conim = opencv.getSnapshot();
contours = opencv.findContours();
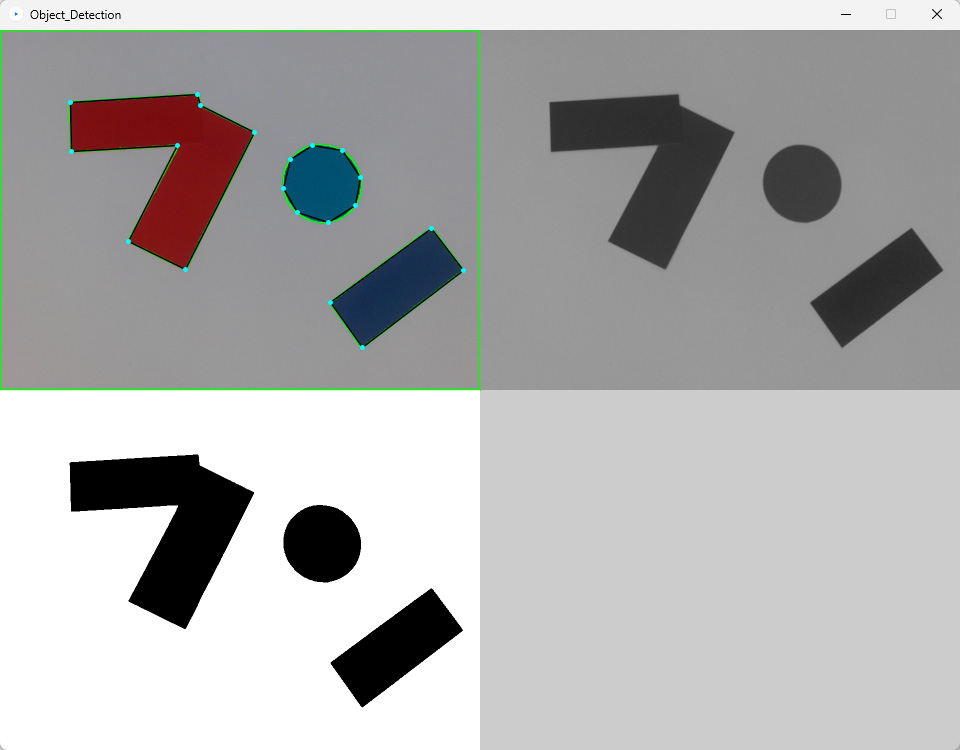
//display the various image adjustments from OpenCV
image(image_holder, 0, 0);
image(bwim, cam.width, 0);
image(conim, 0, cam.height);
noFill();
//the outer loop gets each contour from the list
//of detected contours
for(int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++){
Contour contour = contours.get(i);
strokeWeight(3);
stroke(0, 255, 0);
//this command simply displays the contours
//but you do not have access to the points
contour.draw();
//this sets the resolution of the polygon
//that descirbes each contourbefore you
//put the points into a list for the individual contour
contour.setPolygonApproximationFactor(8);
ArrayList points = contour.getPolygonApproximation().getPoints();
stroke(0);
strokeWeight(3);
//check to see if the contour is the border of the image
if(contour.area() < (w*h)-100){
///draw the polygon
beginShape();
for(int j = 0; j < points.size(); j++){
PVector pt = points.get(j);
vertex(pt.x,pt.y);
}
//you have to complete the shape by adding the
//first vertex.
PVector lpt = points.get(0);
vertex(lpt.x,lpt.y);
endShape();
//draw the vertices
stroke(0,255,255);
strokeWeight(10);
for(int j = 0; j < points.size(); j++){
PVector pt = points.get(j);
point(pt.x,pt.y);
}
}
}
}